All information in the datasheets is also available in ESDL (Energy System Description Language). You can find them in the Energy Data Repository (EDR).
Hydrogen storage – large-scale underground storage in salt caverns
The basic principle of salt cavern storage is the injection of hydrogen into suitable underground salt caverns using compressors. Typically, used pressures range from 80 to 200 bar. The above ground support facilities typically consist of, most importantly, compressors and, next to that, of drying and purification units for the conditioning of extracted hydrogen. These units also make the hydrogen suitable for injection into gas transmission systems and/or end use applications. Depending on the storage concept and end-use targets, above-ground ancillary facilities such as electrolyzers for hydrogen production or combined-cycle gas turbines for electricity production may also be integral parts of salt cavern storage sites. Geometric volumes of 500,000 – 1,000,000 m3 are typical for salt caverns in Europe. Average volumes are reported to be 680.000 m3 (Laban_2020). In the Netherlands, storage sites for hydrogen will likely be connected to the gas transmission system (as it is commonly the case for analogous natural gas storage sites). There are currently no storage facilities combined with hydrogen production or power generation anywhere in the Netherlands, but plans for such hubs are being made (TNO_Internal info).
Downloads
Download hier de datasheet (PDF)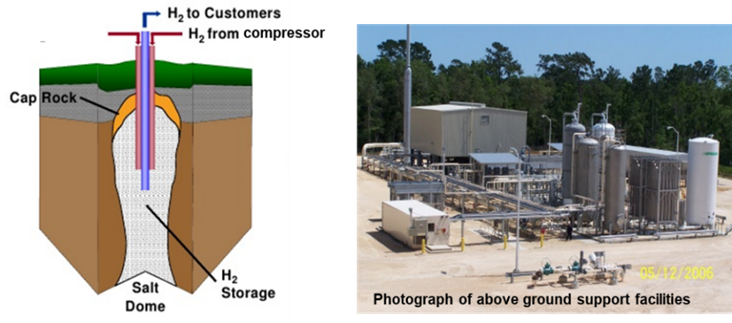
Gerelateerde publicaties

De behoefte aan regelbaar vermogen in 2030-2050
Demand and supply of dispatchable generation in the power system of the Netherlands, 2030-2050

Whitepaper: de waarde van energieopslag
Exploring the value of electricity storage: a comprehensive international overview

Waterstof-opslagbehoefte 2030-2035
Hoeveel opslagcapaciteit is er nodig om aan de waterstofbehoefte te voldoen?