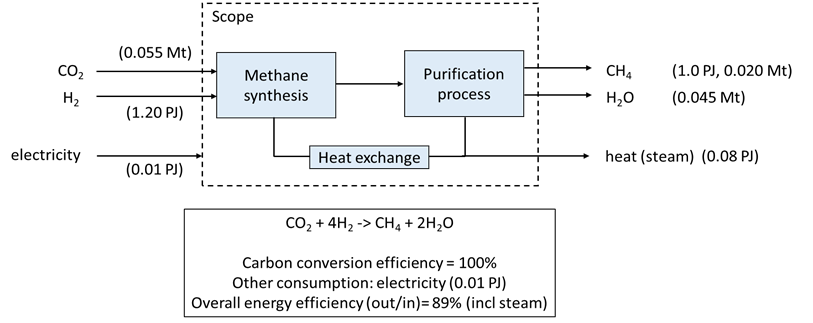
Both H2 and CO2 are provided in this case from external sources. CO2 methanation is a linear combination of CO methanation and reverse water–gas shift reaction and the equilibrium of both reactions is influenced by pressure (1-100 bar) and temperature (200-550 °C). Typically, a couple (2-7) of adiabatic fixed bed reactors are coupled in series to enhance temperature controle and conversion. Intermediate recycles are used to increase carbon conversion efficiency and product yield. To regulate temperature, recycles, and pressures, several compressors and heat-exchangers are integrated in the process.
The product, often called synthetic natural gas (SNG), is mainly methane but may also contain some other gasses, such as H2. Depending on the required purity of the methane, additional purification may be necessary, which can increase costs and energy use. We assume here that methane is produced at sufficient purity for use in other applications. Main developments are occuring in new technological approaches, such as isothermal, sorption enhanced, and fluidised bed methanation. The methanation process is also relevant in the context of bio-SNG production.
All information in the datasheets is also available in ESDL (Energy System Description Language). You can find them in the Energy Data Repository (EDR).